There are two plastics classes thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics:
In polymer, we refer to any polymer that can be molded as plastic; by mold, we mean shaping. Plastics are used in our lives in many applications; there are two classes of plastics: thermoplastics, and thermosetting plastics.
So, what are they, and what is the difference between them?
The two plastics classification are thermoplastic and thermosetting:
The major difference between the two plastic categories; Thermoplastics can be melted after shaping and remolded or reprocessed, where Thermosetting plastics cannot be melted after cooling; they are only molded when first prepared, and can’t be reprocessed.
Let’s look at each class separately:
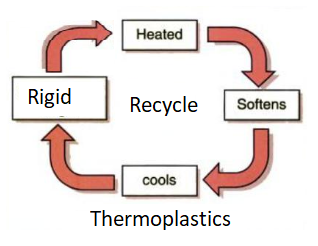
The thermoplastics are polymers that can be melted and shaped when heated. They get soft when heated forming viscous fluid. Their molding or melting process is reversible because it does not involve any chemical bonding.
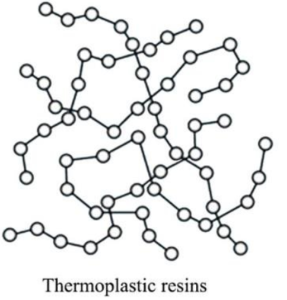
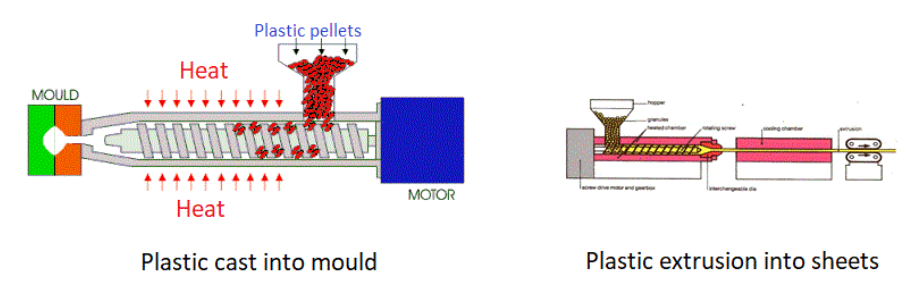
They can be recycled without affecting the physical properties of the polymer. Usually, the thermoplastics polymer is prepared in the shape of pellets that can be fed into a chamber that contains a motor and hydraulic pump. The thermoplastics granules or pellets are heated and melted, then cast into the mold that is used to shape thermoplastics, or extruded through rollers to form sheets.
Thermoplastics examples:
Polyethylene, polypropylene and PVC
Thermoplastics are used in many applications due to their highly recyclable property, high impact resistance, flexibility, ability to be soluble in organic solvents; they can soften without chemical change when heated.
They are used in beverage bottles, plastic food ware, boxes, carpet, and plastic bags.
Thermosetting plastics:
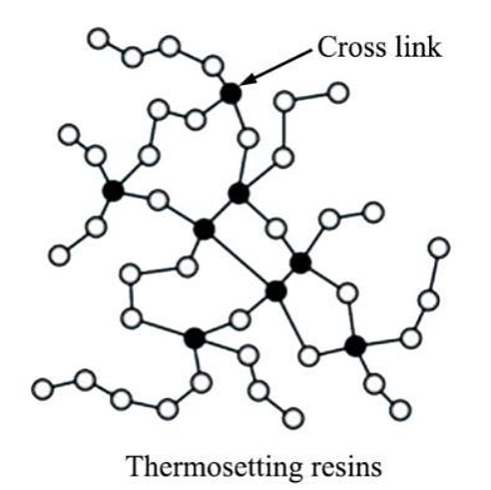
Let’s now look at thermosetting plastics; they are polymers that cannot be reheated to be reshaped, once they are shaped, they cannot be reshaped.
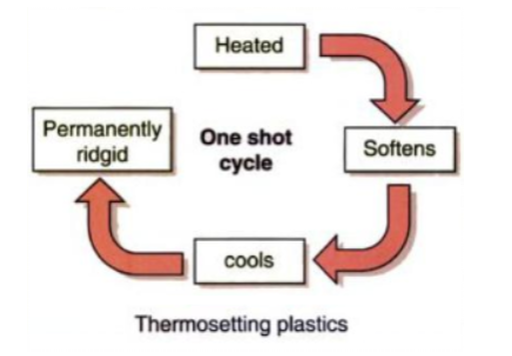
Thermosetting plastics are crosslinked chemically by radiation or crosslinking reagents between molecules during the curing process, which makes the produced plastic very hard, rigid, and can’t be recycled.
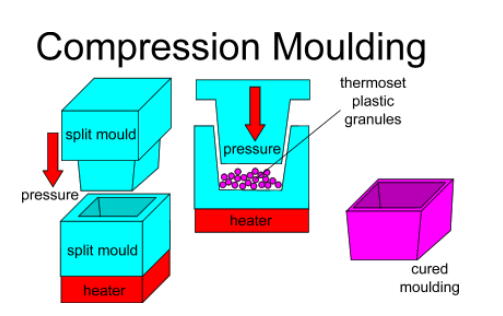
Thermosettings are shaped using the Compression Moulding, where the crosslinking reagent is added at the same time of applying pressure and heat in the split mould.
The formed shapes can’t be recycled and can vary from lot-to-lot due to their crosslinking dependence, and the reactive materials used in their synthesis have an impact on their shelf-life.
Although thermosetting plastics are brittles; they retain their shape when heating; they are light, rigid, and used as a low-cost replacement for metals.
Some types of thermosetting are:
Epoxy, Melamine, silicon, and fiberglass polyesters.
Thermosetting plastics are used in:
Sprockets, batteries cases, and electric applications due to their high isolation and withstanding high temperatures properties.





Leave a comment